CPU
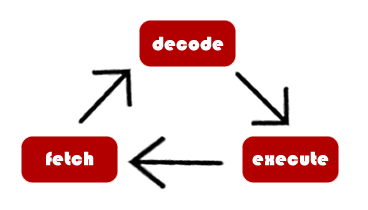
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the part of the computer that processes all the instructions. It is the main component and is central to everything that happens. The CPU is involved with a cycle between it and the memory:
- Fetch - an instruction is fetched from memory.
- Decode - the CPU works out what to do with it.
- Execute - the computer completes the instruction and does whatever it was telling it to do.
- Clock speed - the number of fetch, decode, execute cycles per second. The more the better. A 2GHz CPU has 2,000,000,000 cycles per second.
- Cache - cache is a small amount of super fast memory where the most commonly used instructions can be stored. This means it takes less time to get those instructions. The more cache you have the better.
- Number of cores - having a dual core CPU is a bit like having two CPUs. A quad core is like having four CPUs. The more cores you have the more instructions can be processed at once and the faster your computer will run.
RAM and ROM
| RAM | ROM | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | A temporary storage for the programs that are currently being run. | A permanent storage for the files the computer needs to start up such as the BIOS. |
| Volatility | Volatile - all data is lost when the computer is switched off | Non-volatile - data is saved even when there is no power |
| Measure | Measured in GB e.g. "I have 8GB of RAM" | Not normally measured or mentioned in computer specs. |
| Fact | The more RAM you have the more programs can be run at once. | Original ROM could not be written to but now it is normally possible. |
Input and Output Devices
An input device puts data into a computer system. An output device shows information once it has been processed by the computer. Here are some examples:
| Input Devices | Output Devices |
|---|---|
| Games Controller | Screen / Monitor |
| Number pad | Vibrations |
| Keyboard | Printer |
| Microphone | Sound |
| Mouse | Lights |
| Touchscreen | Projector |
| Movement Sensor | Plotter |
Input Devices for People with Specific Needs
Over the years many people have developed devices to help people with disabilities access computers. Here are some examples:
 |  |  |  |  |
| Speech Recognition | Head Mouse | On Screen Keyboard | Braille Keyboard | Puff Suck Switch |